Article Contents
...
- \n
- Overview \n
- SNMP Trap Scripts Configuration \n
- Trap Receiver Configuration \n
- up.time Configuration \n
...
\nOverview
...
Table of Contents
...
Overview
The purpose of this article is to outline steps to easily deploy a trap listener in your \ninfrastructure infrastructure to drive SNMP trap alerts into up.timeUptime Infrastructure Monitor. Although the article utilizes Trap Receiver \nto snmptrapd provided by Net-SNMP to receive SNMP Traps traps and execute scripts, one can use any SNMP trap receiver as long as it can execute scripts when traps are received.
...
. The steps provided in this article were applied to a Windows server. Identical steps can be applied to a Linux server running Uptime Infrastructure Monitor. Contact Uptime Support at [email protected] if you have any issues.
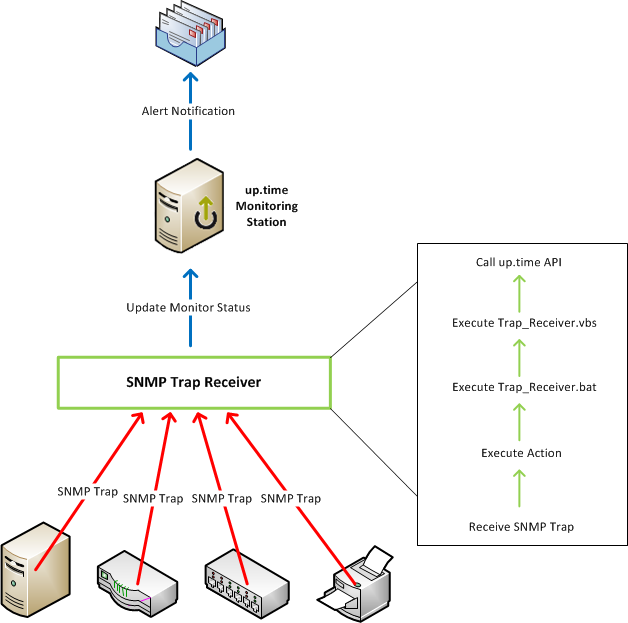
Net-SNMP is an SNMP application suite supported on numerous platforms including Windows and Linux (the two platforms the Uptime Infrastructure Monitor Monitoring Station is supported on). Here \nTrap Receiver is a utility for Windows. If the up.time Monitoring Station is on Windows, you may choose to install it on the same server. \nHere is a brief summary of what happens when an SNMP trap is sent: \n
- \n
- the SNMP-enabled device sends an SNMP trap to the SNMP Trap Receiver \n
- Trap Receiver reviews the list of configured Actions and executes Action(s) if the trap meets the filter \n
- the Trap Receiver Action executes the Trap_Receiver.bat script, which is a wrapper for Trap_Receiver.vbs \n
- snmptrapd service
- snmptrapd compares the trap to the list of filters in the snmptrapd.conf file
- when the trap matches the uptime filter, the trap_to_ext_event.pl perl script is executed
- trap_to_ext_event.pl calls the Uptime Infrastructure Monitor Trap_Receiver.vbs calls up.time API to update the status of the External Check monitor associated with the device \n
- if an Alert Profile is associated with the monitor, an alert notification is sent out \n
...
Below is a diagram depicting the process:
...
\n \n \n
...
\nSNMP Trap Scripts Configuration
...
- \n
- Download the SNMP Trap Receiver Scripts \n
- Extract Trap_Receiver_Scripts.zip file \n
- Put the files in an appropriate directory (e.g. C:uptime) \n
- Open Trap_Receiver.bat and look for the “SCRIPT_DIR” variable. Change it to where you have put the scripts in step 2. \n
- Open Trap_Receiver.vbs and modify a few variables if needed: \n
- \n
MonitoringStationHost
\n…this is where the up.time Monitoring Station is installed. Make certain the hostname/IP used can communicate from where the scripts are to the Monitoring Station. \n \nMonitoringStationPort
\n…this is the port up.time uses for the API. By default it’s 9996. \n \nAlertStatus
\n
\n…this is the severity of the alert in up.time when an SNMP trap is received.
\n\nThe value can be one of the following integers:
\n- \n
- 0=OK \n
- 1=Warning \n
- 2=Critical \n
- 3=Unknown \n
\n \n
\n
...
\nTrap Receiver Configuration
...
...
Install Net-SNMP and Perl
- Download Net-SNMP from http://sourceforge.net/projects/net-snmp/files/net-snmp%20binaries/5.6.1.1-binaries/net-snmp-5.6.1.1-1.x86.exe/download
- Download Strawberry Perl from http://strawberryperl.com/download/5.20.1.1/strawberry-perl-5.20.1.1-64bit.msi
- Execute the Net-SNMP installer and accept the defaults.
- Execute the Strawberry Perl installer and accept the defaults
...
Create a snmptrapd configuration file and Perl script
create a new file called snmptrapd.conf in the C:\usr\etc\snmp directory with contents similar to the following ("public" on the first line is the SNMP community string - feel free to changed accordingly, and the path to Uptime Infrastructure Monitor on the second line should be changed accordingly):
Code Block authCommunity log,execute,net public traphandle default C:\Strawberry\perl\bin\perl.exe "C:\Program Files\uptime software\uptime\scripts\snmp-trap-script\trap_to_ext_event.pl"- in the Start menu, select the Net-SNMP folder, right click Register Trap Service and choose Run As Administrator
- start the "Net-SNMP Trap Handler" service
- create the directory "C:\Program Files\uptime software\uptime\scripts\snmp-trap-script"
- download and copy this file, trap_to_ext_event.pl, to the directory mentioned in the previous step
This approach assumes that your SNMP trap service monitors all have the same name, "SNMP Trap (member)", and are managed via a Service Group.
There are two logs that are created with this solution, one when traps are received by the Net-SNMP Trap Handler service and another when the trap is sent into Uptime Infrastructure Monitor by the perl script. This helps to narrow down an issue if one arises.
...
Uptime Infrastructure Monitor Configuration
Create a new monitor called "SNMP Trap" and assign it to a Service Group, so that it can be applied to numerous Elements in Uptime Infrastructure Monitor.
- Create a Service Group for your devices that will send SNMP traps to Uptime Infrastructure Monitor.
- Click on the “Services” button at the top
- Click the "Add Service Group" link in the menu on the left
- Select "Regular" from the drop down and click the "Continue..." button
- Enter "SNMP Trap Group" as the name for the Service Group and, optionally, a description for the group
- In the "Available Element Groups" and "Available Elements" lists, choose the Element Groups and Elements that you want to have SNMP Trap monitors created for
- Click the "Finish" button and close the dialogue window
- Create an External Check monitor and assign it to the "SNMP Trap Group" Service Group.
- Download Trap Receiver from the following website: \n \n \n
- Install Trap Receiver \n
- Launch the Trap Receiver UI \n
- Click on the “Configure” button: \n
\n \n
\n - You should be at the “Actions” tab. Click “Add”: \n
\n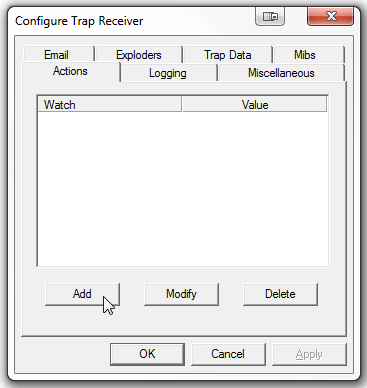 \n
\n - Since the IP of the device sending out SNMP traps might be displayed differently in up.time, a separate action should be created for each device so that the proper hostname can be passed to up.time. \n
\nTo add a new action tied to a particular IP: \n- \n
- Under “Watch”, select “Sender IP”. \n
- Under “Equals”, input the IP Address of the device that will be sending the SNMP Traps. \n
- Check the “Execute” checkbox and click “Configure” \n
- Click on the “…” button and select the “Trap_Receiver.bat” from SNMP Trap Scripts Configuration Step 2 \n
- In the Arguments box, type the following: \n
\n--hostname=yourDeviceName \n\n…where “yourDeviceName” is the “Host Name” in up.time. The “Host Name” can be found under the “Info” tab in up.time. For example: \n
\n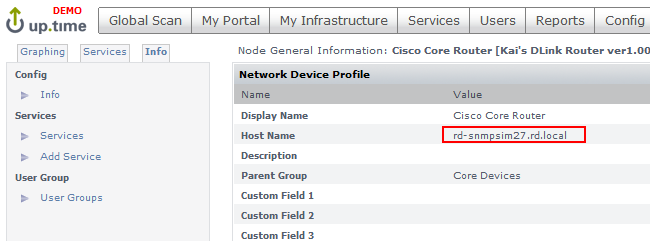 \n
\n - Check the “Include Trap Data” checkbox. See below: \n
- Click “OK” \n
- Click “Update” to get back to the Configure Trap Receiver window. \n
\n
\n
- Go to the “Trap Data” tab \n
- \n
- Check the “Pass to Command Line” checkbox \n
- Click “Specify Parameters” \n
\n \n
\n - Make sure the following lines are checked and the Command Line Flags are as follow: \n
\n
\n \nThe end result should look like this: \n\n
\n \nVariable \nCommand Line Flags \n\n \nIp Address \t \nIpAddress \n\n \nVarbind Data \nVarbindData \n\n \nVarbind OID \nVarbindOID \n
\n \n
\n - Click “OK” when complete \n
- The SNMP variables, by default, will be shown as numbers (e.g. 1.3.6…). To show more meaningful variable names, you will need to load the appropriate MIBs from your devices.
\nGo to the “Mibs” tab in the “Configure Trap Receiver” window \n- \n
- Check the “Translate OIDs” checkbox \n
- Obtain vendor-specific MIBs and load them by clicking the “Load MIB” button \n
\n \n
\n - Click “OK” when finish loading MIBs \n
\nup.time Configuration
\n \n \nAdd an “External Check” Service Monitor in up.time: \n- \n
- Click on the “Services” button at the top \n
- Click “Add Service Monitor” on the left \n
- Select “External Check” from the list of available Service Monitors and click “Continue…” \n
- Input “SNMP - Trap” as the Service Name \n
- From the drop down menu where it says "Select a System", select the host/device that will be sending the SNMP trap \n
- Click “Finish” \n
- Select the "Service Group" radio button and choose "SNMP Trap Group" from the drop down.
- Choose an Alert Profile to have alert messages sent to the appropriate users.
- Click “Finish”
Now when traps are received by the Net-SNMP snmptrapd service, the appropriate "SNMP Trap (member)" service monitor will be set to CRIT and an alert will be sent out. When the status is acknowledged in the Uptime Infrastructure Monitor UI (click the ACK button), the status will be set back to OK.